前言
Lua 栈是LuaState的核心,它维护了Lua函数调用的上下文信息,充当C与Lua通信的”桥梁“,本文介绍Lua Stack结构,核心相关function实现。
Lua Stack内存结构
LuaState 是一个Luavm的实例,不同的LuaState拥有不同的调用栈,而其中的调用栈实现就是:Lua Stack。Stack的实现是一个TValue数组,索引从0开始递增,每次有push或者相关可能增大Lua栈的操作,就会去检查是否需要栈扩展,确保能保存即将发生的上下文信息。LuaState中有几个核心的成员,记录着和栈相关的数据:
- StkId stack: 栈数组的base指针
- StkId top; 栈的top指针,指向数组最后一个元素的下一个地址
- StkId stack_last: 当栈增长时,top最终指向栈的最高点,stack_last指向最新的未被使用的位置
- int stacksize: 栈的size
typedef TValue *StkId; /* index to stack elements */
struct lua_State {
CommonHeader;
unsigned short nci; /* number of items in 'ci' list */
lu_byte status;
StkId top; /* first free slot in the stack */
global_State *l_G;
CallInfo *ci; /* call info for current function */
const Instruction *oldpc; /* last pc traced */
StkId stack_last; /* last free slot in the stack */
StkId stack; /* stack base */
UpVal *openupval; /* list of open upvalues in this stack */
GCObject *gclist;
struct lua_State *twups; /* list of threads with open upvalues */
struct lua_longjmp *errorJmp; /* current error recover point */
CallInfo base_ci; /* CallInfo for first level (C calling Lua) */
volatile lua_Hook hook;
ptrdiff_t errfunc; /* current error handling function (stack index) */
int stacksize;
int basehookcount;
int hookcount;
unsigned short nny; /* number of non-yieldable calls in stack */
unsigned short nCcalls; /* number of nested C calls */
l_signalT hookmask;
lu_byte allowhook;
};
标准栈的读写,应该只提供pop/push,但Lua栈实际提供了基于index访问的实现,index分为正/负:
- index > 0 : 从栈底向上索引,即 lua_State.stack + index
- index < 0 : 从栈顶往下索引, 即 lua_State.top + index
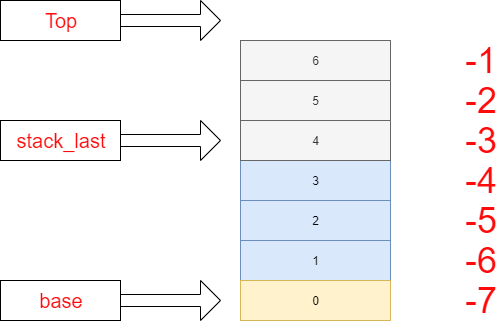
一个简单的栈实例图如下:
- 0:在lua栈中的存放的是当前调用的func
- 1-3: 存放当前func的上下文信息,参数/返回值等等
- 4-6: 增长的栈,尚未使用
Stack核心function
Lua与C的通信接口主要维护在lauxlib.c/lapi.c文件中:
- lauxlib.c 维护一下高级接口,如:luaL_newstate()/luaL_openlib()等
- lapi.c 维护一些更底层的接口:如:lua_isstring()/lua_tointegerx()等
总体上对栈的操作分三种:类型检查(lua_isxxxx), 取值类(lua_toxxxx), 修改栈(lua_setXXX/lua_getxxxxx…)
lua_isxxxx
- 检测栈对应的索引是否是xxx类型,非常简单,不赘诉了
LUA_API int lua_isinteger (lua_State *L, int idx) {
StkId o = index2addr(L, idx);
return ttisinteger(o);
}
lua_toXXX操作
- index2addr 是通过索引访问lua栈的最底层接口,几乎所有lua_toxxxx方法都会用到它。
- ci->func:每个栈帧的相对0点位置,后面栈的操作都是基于此的偏移
- api_check(L,xxx): 对索引临界值校验,严格保证一个栈帧只能操作它自己的栈范围
- LUA_REGISTRYINDEX:lua为了统一取值接口,做了伪索引的概念,index=LUA_REGISTRYINDEX时,实际取得是全局注册表
- index < LUA_REGISTRYINDEX: 实际上操作的是lua的upvalue
static TValue *index2addinr (lua_State *L, int idx) {
CallInfo *ci = L->ci;
if (idx > 0) {
TValue *o = ci->func + idx;
api_check(L, idx <= ci->top - (ci->func + 1), "unacceptable index");
if (o >= L->top) return NONVALIDVALUE;
else return o;
}
else if (!ispseudo(idx)) { /* negative index */
api_check(L, idx != 0 && -idx <= L->top - (ci->func + 1), "invalid index");
return L->top + idx;
}
else if (idx == LUA_REGISTRYINDEX)
return &G(L)->l_registry;
else { /* upvalues */
idx = LUA_REGISTRYINDEX - idx;
api_check(L, idx <= MAXUPVAL + 1, "upvalue index too large");
if (ttislcf(ci->func)) /* light C function? */
return NONVALIDVALUE; /* it has no upvalues */
else {
CClosure *func = clCvalue(ci->func);
return (idx <= func->nupvalues) ? &func->upvalue[idx-1] : NONVALIDVALUE;
}
}
}
- lua_tonumberx 可以注意到仅仅封装一下index2addinr方法,并没有太多逻辑,类似操作lua_tointegerx/lua_toboolean…
LUA_API lua_Number lua_tonumberx (lua_State *L, int idx, int *pisnum) {
lua_Number n;
const TValue *o = index2addr(L, idx);
int isnum = tonumber(o, &n);
if (!isnum)
n = 0; /* call to 'tonumber' may change 'n' even if it fails */
if (pisnum) *pisnum = isnum;
return n;
}
lua_getxxxxx
此类func,虽然命名以getxxx为前缀,但并不是直接从栈中取某个索引的对象,而是操作指定索引处的table,然后push到栈中。
- lua_getfield: 取栈idx对应的table->用指定k查对应table中的val->把val插入栈顶
LUA_API int lua_getfield (lua_State *L, int idx, const char *k) {
lua_lock(L);
return auxgetstr(L, index2addr(L, idx), k);
}
static int auxgetstr (lua_State *L, const TValue *t, const char *k) {
const TValue *slot;
TString *str = luaS_new(L, k);
if (luaV_fastget(L, t, str, slot, luaH_getstr)) {
setobj2s(L, L->top, slot);
api_incr_top(L);
}
else {
setsvalue2s(L, L->top, str);
api_incr_top(L);
luaV_finishget(L, t, L->top - 1, L->top - 1, slot);
}
lua_unlock(L);
return ttnov(L->top - 1);
}
- lua_gettable 这个func稍有点特殊:取栈idx对应的table->当前栈顶的k查对应table中的val->把val插入栈顶
LUA_API int lua_gettable (lua_State *L, int idx) {
StkId t;
lua_lock(L);
t = index2addr(L, idx);
luaV_gettable(L, t, L->top - 1, L->top - 1);
lua_unlock(L);
return ttnov(L->top - 1);
}
lua_setxxxx
大多数也是操作stack中table,用当前栈中的值,去往指定索引处的table设值
- lua_setfield 取栈idx处table->用指定的key(const char *k)+ 当前栈顶的val-> 向table中设值
LUA_API void lua_setfield (lua_State *L, int idx, const char *k) {
lua_lock(L); /* unlock done in 'auxsetstr' */
auxsetstr(L, index2addr(L, idx), k);
}
static void auxsetstr (lua_State *L, const TValue *t, const char *k) {
const TValue *slot;
TString *str = luaS_new(L, k);
api_checknelems(L, 1);
if (luaV_fastset(L, t, str, slot, luaH_getstr, L->top - 1))
L->top--; /* pop value */
else {
setsvalue2s(L, L->top, str); /* push 'str' (to make it a TValue) */
api_incr_top(L);
luaV_finishset(L, t, L->top - 1, L->top - 2, slot);
L->top -= 2; /* pop value and key */
}
lua_unlock(L); /* lock done by caller */
}
- lua_settable 栈idx处的table-> top-2作key,top - 1作val ->设table
LUA_API void lua_settable (lua_State *L, int idx) {
StkId t;
lua_lock(L);
api_checknelems(L, 2);
t = index2addr(L, idx);
luaV_settable(L, t, L->top - 2, L->top - 1);
L->top -= 2; /* pop index and value */
lua_unlock(L);
}
lua_rotate
设计上比较有意思的一个func,实际上是leetcode一个经典的三次反转算法,大致做用:从栈idx到top范围,旋转n个元素,如果n>0则正向旋转,反之负向旋转,案例图:
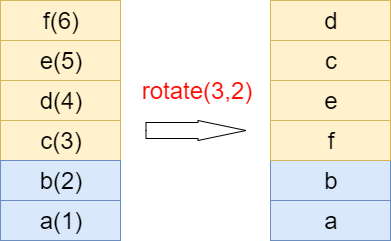
LUA_API void lua_rotate (lua_State *L, int idx, int n) {
StkId p, t, m;
lua_lock(L);
t = L->top - 1; /* end of stack segment being rotated */
p = index2addr(L, idx); /* start of segment */
api_checkstackindex(L, idx, p);
api_check(L, (n >= 0 ? n : -n) <= (t - p + 1), "invalid 'n'");
m = (n >= 0 ? t - n : p - n - 1); /* end of prefix */
reverse(L, p, m); /* reverse the prefix with length 'n' */
reverse(L, m + 1, t); /* reverse the suffix */
reverse(L, p, t); /* reverse the entire segment */
lua_unlock(L);
}
lua_insert和lua_remove的实现都是基于rotate
#define lua_insert(L,idx) lua_rotate(L, (idx), 1)
#define lua_remove(L,idx) (lua_rotate(L, (idx), -1), lua_pop(L, 1))
C和lua通信hello world
#include <stdio.h>
#include "lua.h"
#include "lauxlib.h"
#include "lualib.h"
int c_lua_helloworld(lua_State *L) {
const char * hw = lua_tostring(L, -1);
printf("%s\n", hw);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
lua_State *L = luaL_newstate(); /* create state */
luaL_openlibs(L);
lua_register(L, "c_lua_helloworld", c_lua_helloworld);
luaL_dostring(L, "c_lua_helloworld('hello world!!')");
return 0;
}